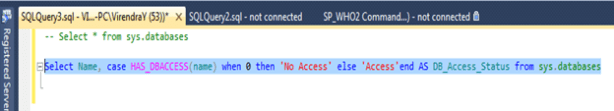
To transfer logins between servers and retain the logins’ passwords (SQL Logins), consider utilizing the DTS task to transfer logins between servers, or use the following SQL statement:
select ‘sp_addlogin @loginame = ‘ + name + ‘, @passwd = ”’ + password + ”’, @encryptopt = skip_encryption, @deflanguage = ”’ + language + ”” from sys.syslogins
or as per BOL/MSDN, we can use
USE master
GO
IF OBJECT_ID (‘sp_hexadecimal’) IS NOT NULL
DROP PROCEDURE sp_hexadecimal
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_hexadecimal
@binvalue varbinary(256),
@hexvalue varchar (514) OUTPUT
AS
DECLARE @charvalue varchar (514)
DECLARE @i int
DECLARE @length int
DECLARE @hexstring char(16)
SELECT @charvalue = ‘0x’
SELECT @i = 1
SELECT @length = DATALENGTH (@binvalue)
SELECT @hexstring = ‘0123456789ABCDEF’
WHILE (@i <= @length)
BEGIN
DECLARE @tempint int
DECLARE @firstint int
DECLARE @secondint int
SELECT @tempint = CONVERT(int, SUBSTRING(@binvalue,@i,1))
SELECT @firstint = FLOOR(@tempint/16)
SELECT @secondint = @tempint – (@firstint*16)
SELECT @charvalue = @charvalue +
SUBSTRING(@hexstring, @firstint+1, 1) +
SUBSTRING(@hexstring, @secondint+1, 1)
SELECT @i = @i + 1
END
SELECT @hexvalue = @charvalue
GO
IF OBJECT_ID (‘sp_help_revlogin’) IS NOT NULL
DROP PROCEDURE sp_help_revlogin
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_help_revlogin @login_name sysname = NULL AS
DECLARE @name sysname
DECLARE @type varchar (1)
DECLARE @hasaccess int
DECLARE @denylogin int
DECLARE @is_disabled int
DECLARE @PWD_varbinary varbinary (256)
DECLARE @PWD_string varchar (514)
DECLARE @SID_varbinary varbinary (85)
DECLARE @SID_string varchar (514)
DECLARE @tmpstr varchar (1024)
DECLARE @is_policy_checked varchar (3)
DECLARE @is_expiration_checked varchar (3)
DECLARE @defaultdb sysname
IF (@login_name IS NULL)
DECLARE login_curs CURSOR FOR
SELECT p.sid, p.name, p.type, p.is_disabled, p.default_database_name, l.hasaccess, l.denylogin FROM sys.server_principals p
LEFT JOIN sys.syslogins l ON ( l.name = p.name ) WHERE p.type IN ( ‘S’, ‘G’, ‘U’ ) AND p.name <> ‘sa’
ELSE
DECLARE login_curs CURSOR FOR
SELECT p.sid, p.name, p.type, p.is_disabled, p.default_database_name, l.hasaccess, l.denylogin FROM sys.server_principals p
LEFT JOIN sys.syslogins l ON ( l.name = p.name ) WHERE p.type IN ( ‘S’, ‘G’, ‘U’ ) AND p.name = @login_name
OPEN login_curs
FETCH NEXT FROM login_curs INTO @SID_varbinary, @name, @type, @is_disabled, @defaultdb, @hasaccess, @denylogin
IF (@@fetch_status = -1)
BEGIN
PRINT ‘No login(s) found.’
CLOSE login_curs
DEALLOCATE login_curs
RETURN -1
END
SET @tmpstr = ‘/* sp_help_revlogin script ‘
PRINT @tmpstr
SET @tmpstr = ‘** Generated ‘ + CONVERT (varchar, GETDATE()) + ‘ on ‘ + @@SERVERNAME + ‘ */’
PRINT @tmpstr
PRINT ”
WHILE (@@fetch_status <> -1)
BEGIN
IF (@@fetch_status <> -2)
BEGIN
PRINT ”
SET @tmpstr = ‘– Login: ‘ + @name
PRINT @tmpstr
IF (@type IN ( ‘G’, ‘U’))
BEGIN — NT authenticated account/group
SET @tmpstr = ‘CREATE LOGIN ‘ + QUOTENAME( @name ) + ‘ FROM WINDOWS WITH DEFAULT_DATABASE = [‘ + @defaultdb + ‘]’
END
ELSE BEGIN — SQL Server authentication
— obtain password and sid
SET @PWD_varbinary = CAST( LOGINPROPERTY( @name, ‘PasswordHash’ ) AS varbinary (256) )
EXEC sp_hexadecimal @PWD_varbinary, @PWD_string OUT
EXEC sp_hexadecimal @SID_varbinary,@SID_string OUT
— obtain password policy state
SELECT @is_policy_checked = CASE is_policy_checked WHEN 1 THEN ‘ON’ WHEN 0 THEN ‘OFF’ ELSE NULL END FROM sys.sql_logins WHERE name = @name
SELECT @is_expiration_checked = CASE is_expiration_checked WHEN 1 THEN ‘ON’ WHEN 0 THEN ‘OFF’ ELSE NULL END FROM sys.sql_logins WHERE name = @name
SET @tmpstr = ‘CREATE LOGIN ‘ + QUOTENAME( @name ) + ‘ WITH PASSWORD = ‘ + @PWD_string + ‘ HASHED, SID = ‘ + @SID_string + ‘, DEFAULT_DATABASE = [‘ + @defaultdb + ‘]’
IF ( @is_policy_checked IS NOT NULL )
BEGIN
SET @tmpstr = @tmpstr + ‘, CHECK_POLICY = ‘ + @is_policy_checked
END
IF ( @is_expiration_checked IS NOT NULL )
BEGIN
SET @tmpstr = @tmpstr + ‘, CHECK_EXPIRATION = ‘ + @is_expiration_checked
END
END
IF (@denylogin = 1)
BEGIN — login is denied access
SET @tmpstr = @tmpstr + ‘; DENY CONNECT SQL TO ‘ + QUOTENAME( @name )
END
ELSE IF (@hasaccess = 0)
BEGIN — login exists but does not have access
SET @tmpstr = @tmpstr + ‘; REVOKE CONNECT SQL TO ‘ + QUOTENAME( @name )
END
IF (@is_disabled = 1)
BEGIN — login is disabled
SET @tmpstr = @tmpstr + ‘; ALTER LOGIN ‘ + QUOTENAME( @name ) + ‘ DISABLE’
END
PRINT @tmpstr
END
FETCH NEXT FROM login_curs INTO @SID_varbinary, @name, @type, @is_disabled, @defaultdb, @hasaccess, @denylogin
END
CLOSE login_curs
DEALLOCATE login_curs
RETURN 0
GO
— Run SP to get Scripts
EXEC sp_help_revlogin